It’s no secret that magnets are in nearly everything we use on a regular basis.
But what type of magnets are they? And which type of magnet is best for a particular situation?
In this blog, we’ll take a deeper look into the differences between electromagnets and permanent magnets.
Permanent Magnets
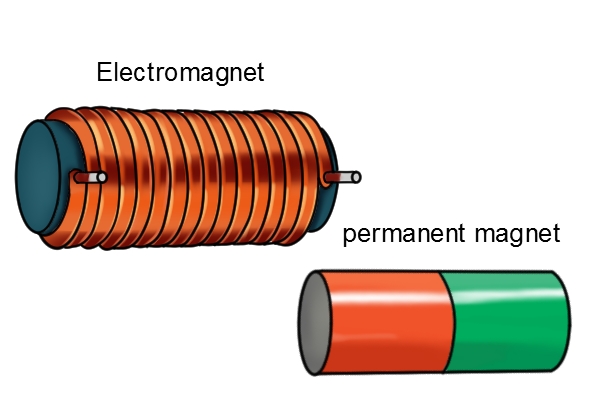
Permanent magnets are made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field.
This type of magnet always has a magnetic field and will display that magnetic and attractive behaviour at all times.
Just as the name suggests, permanent magnets consist of magnetic material whose atoms have been permanently aligned to create a persistent magnetic field.
Permanent magnets can be made of various materials including:
It’s important to note that Neodymium and Samarium Cobalt magnets are also classified as Rare Earth magnets, which means that they have superior holding strength in comparison to its physical size.
Electromagnets
As indicated by its name, an electromagnet operates and is dependent on electricity.
An electromagnet is a type of magnet whose magnetic field is created by the flow of an electric current.
The magnetic force in electromagnets is activated when electricity is turned on, and stops as soon as the electrical current is disconnected.
This type of magnet is made from a coil of wire, which acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it. Oftentimes, an electromagnet is made stronger by wrapping it around a core of material like steel, which enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.
Electromagnets offer the advantages of controlled holding power, and through the application of controlled DC electrical current, they have the ability to attract and hold ferrous materials with varying degrees of force.
What Are The Differences Between Electromagnets and Permanent Magnets?
The two major differences between electromagnets and permanent magnets are:
1. Loss of properties
2. Magnetic strength
With very few exceptions, such as exceeding maximum operating temperatures, permanent magnets remain magnetized constantly, while electromagnets are reliant on electrical currents for the strength of their magnetic properties.
Magnetic strength is dependent on various factors.
The magnetic strength of permanent magnets depends on the overall material, size, and shape of the magnet itself, but once that level of magnetization is determined, it does not change.
Electromagnets, on the other hand, are highly dependent on the electrical current supplied. Meaning, electromagnets can provide multiple magnetic strengths.
Pros & Cons
|
|
Electromagnets |
Permanent Magnets |
|
Pros |
Able to manipulate their magnetic pull strength by turning the magnet or off, or by adjusting the electrical current Greater pull strength |
Able to operate without a power supply, making them energy efficient and portable Available in very small dimensions make them ideal for size-limited applications |
|
Cons |
Since significant amounts of coiling is needed to create strong magnetic fields, their size can be prohibitive in some applications Supplying too much current can create shorts, rendering the magnet useless. |
Lose strength in very hot environments, and are therefore unsuitable for some applications Fixed magnetic pull can make them unattractive to users looking for flexibility with their magnets |
The Verdict?
Ultimately, the choice is up to you regarding which magnet you decide to go with.
Whether you choose electromagnets or permanent magnets for your application, be sure you fully understand the pros and cons of each.
Need More Information?
If you need help deciding which magnet is best for you, give us a call. One of our experts will be more than happy to assist!